Are you confident on questions about money and banking? Did you know there different types of banks in India? In terms of the government test syllabus, a candidate must understand the many types of banks and their roles in administering a country's financial system. Banks are financial institutions that deal with deposits and loans. In India, there are several different sorts of banks, each with its own set of responsibilities. The bank accepts deposits from the public at a considerably lower rate, known as the deposit rate, and lends money at a much higher rate, known as the lending rate. The fundamental duties of banks are nearly identical, however, the types of persons with whom each sector or type deals may vary. In India, modern banking originated in the late eighteenth century. The 'Bank Of Calcutta,' founded in 1806 and currently known as the 'State Bank Of India,' is the country's oldest profit-oriented bank. In India, there are currently 34 banks, with 12 public sector banks and 22 private sector banks. Banks have aided the country's economic development and developed a culture of saving among its citizens. Let's have a look at the different types of banks in India. The space below contains the list of different types of banks in India. If you are preparing for competitive exams and are looking for expert guidance, you can check out Bank Special Online Classes: Join Detailed Batch By Safalta here!
Banks are divided into several sorts. The following are the different types of banks in India:
Central Bank
Cooperative Banks
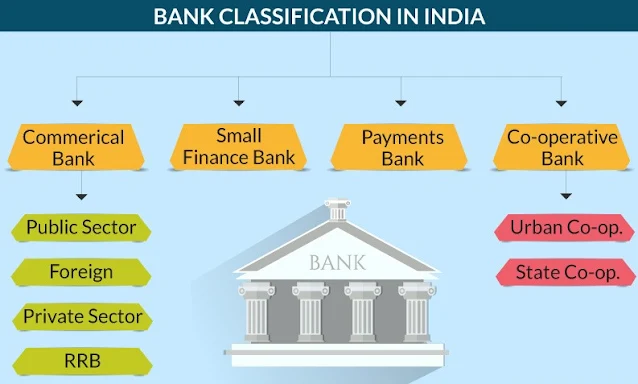
Commercial Banks
Regional Rural Banks (RRB)
Local Area Banks (LAB)
Specialized Banks
Small Finance Banks
Payments Banks
This is a crucial subject for the IAS Exam. Aspirants will learn about the Indian banking system, its functions, and the different types of banks in this article.
The several types of banks in India, their functions, and a list of banks under each sector are all part of the banking
Central Bank:
Our country's central bank is the Reserve Bank of India. Each country has a central bank that oversees all of the country's other financial institutions.
The central bank's principal role is to serve as the government's bank and to oversee and regulate the country's other banking institutions. The functions of a country's central bank are listed below:
assisting other financial institutions
Issuing money and enforcing monetary policies
The financial system's supervisor
In other words, the country's central bank is also known as the banker's bank because it assists other banks in the country and runs the country's financial system under the supervision of the Government.
Cooperative Banks:
These banks are governed by a law enacted by the state government. They provide short-term loans to agriculture and related industries.
Cooperative banks' principal purpose is to enhance social welfare by providing low-interest loans.
They are arranged in a three-tiered system.
State Cooperative Banks, Tier 1 (State Level) (regulated by RBI, State Govt, NABARD)
The RBI, the government, and the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) all contribute to the project's funding. After then, the money is allocated to the general population.
These banks are subject to CRR and SLR concessions. (SLR: 25%, CRR: 3%)
The state owns the company, and the senior management is chosen by the members.
Central/District Cooperative Banks, Tier 2 (District Level)
Tier 3 (Village Level) – Agriculture (Primary) Cooperative Banks
Commercial Banks:
The Banking Companies Act of 1956 established the company.
They function on a commercial basis, with profit as their primary goal.
They are owned by the government, state, or any private company and have a unified structure.
They look after all sectors, from rural to urban.
Unless the RBI directs otherwise, these banks do not charge concessional interest rates.
These banks' primary source of funds is public deposits.
Commercial banks are further classified into three types:
Public sector banks are those in which the government or the country's central bank owns the majority of the stock.
Banks in the private sector are those in which a private entity, an individual, or a group of people owns the majority of the stock.
Foreign Banks – This category includes banks with headquarters in other nations and branches in the United States.
Regional Rural Banks (RRB):
These are unique types of commercial banks that lend to agriculture and the rural economy at a reduced rate.
RRBs were founded in 1975 and are governed by the 1976 Regional Rural Bank Act.
RRBs are 50/50 joint ventures between the federal government and state governments (15%), as well as commercial banks (35 percent ).
Between 1987 and 2005, 196 RRBs were established.
From 2005 forward, the government began merging RRBs, bringing the total number of RRBs to 82.
A single RRB cannot open branches in more than three districts that are geographically connected.
Local Area Banks (LAB):
In India, it was first introduced in 1996.
The private sector organizes these.
Local Area Banks' primary goal is to make a profit.
Local Area Banks are governed by the 1956 Companies Act.
There are now just four Local Area Banks in existence, all of which are located in South India.
Specialized Banks:
Certain banks exist just to serve a certain purpose. Specialized banks are the name for several types of financial institutions. These are some of them:
SIDBI (Small Industries Development Bank of India) - SIDBI can provide a loan for a small-scale enterprise or business. With the support of this bank, small businesses can get current technology and equipment.
Export and Import Bank (EXIM Bank) - EXIM Bank stands for Export and Import Bank. This type of bank can provide loans or other financial help to foreign countries that are exporting or importing goods.
NABARD (National Bank for Agricultural and Rural Development) – People can resort to NABARD for any type of financial support for rural, handicraft, village, and agricultural development.
Other specialist banks exist, each with a unique function to play in the financial development of the country.
Small Finance Banks:
This sort of bank, as the name implies, provides loans and financial help to micro industries, small farmers, and the unorganized sector of society. The country's central bank oversees these institutions
Payments Banks:
The Reserve Bank of India conceptualized the payments bank, a newly developed form of banking. People who have a payment bank account can only deposit up to Rs.1,00,000/- and cannot apply for loans or credit cards through this account.
Payment banks provide services such as internet banking, mobile banking, ATM card issuance, and debit card issuance. The following is a list of our country's few payment banks:
Airtel Payments Bank
India Post Payments Bank
Fino Payments Bank
Jio Payments Bank
Paytm Payments Bank
NSDL Payments Bank






If a counter is hit, it's not positioned on the bar, however instead, the hitting piece is positioned on high, and the purpose is then controlled by the hitting player. The counter which has been hit is 'imprisoned' and can't be moved until the opponent removes his piece. Sometimes, a rule is used that requires a player to convey his first counter around to his residence board before shifting any others. In any case, a fast advance a minimum of} one|to 1}'s own residence 카지노사이트 board is desirable, as imprisoning the opponent's counter might be} extremely advantageous. There are two video games recognized as|often known as} sugoroku (双六) in Japan.
ReplyDelete